Next: Ravel Classes Up: Javascript API for Ravel Previous: Getting Started
A ravel provides a way of manipulating 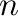 -dimensional datasets. Each
dimension is controlled by a handle, which looks like an
arrow. The dimensionality of the ravel's output data is called the
rank. Typical applications might have a rank 1 ravel (for
controlling plots or timeseries) or rank 2 (for controlling
spreadsheets or surface plots).
-dimensional datasets. Each
dimension is controlled by a handle, which looks like an
arrow. The dimensionality of the ravel's output data is called the
rank. Typical applications might have a rank 1 ravel (for
controlling plots or timeseries) or rank 2 (for controlling
spreadsheets or surface plots).
Handles may be output handles, which control the dimensions of the output dataset, or other, non-output handles. Handles may be swapped by rotating the handle, potentially turning an output handle into a non-output handle and vice-versa. A non-output handle will have a slicer control, which control which slice is output by the ravel. The labels along a handle are known as slice labels.
When a handle is collapsed (by dragging the handle tip towards the origin), the entire dataset is reduced along that dimension by applying an arithmetic operation between the values. Reduction operations include sum, product, average, standard deviation, minimum and maximum.